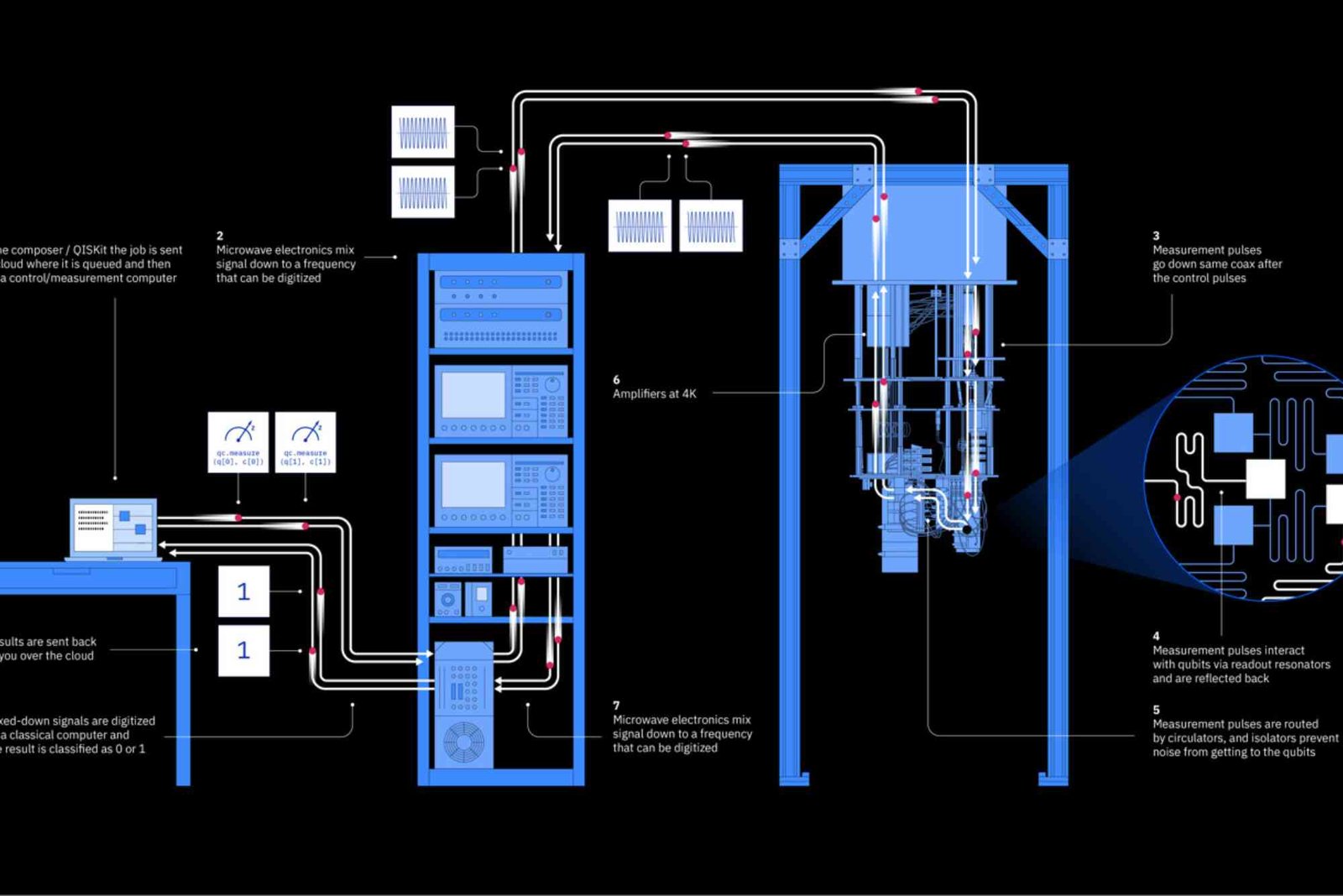
Quantum computing is revolutionizing the way we think about computation. Unlike classical computers that rely on bits as 0s or 1s, quantum computers leverage the strange yet powerful properties of quantum mechanics. By understanding how quantum computing works, we can explore its potential to solve problems that classical computers cannot handle efficiently. In this article, we’ll break down the principles behind quantum computing, how it functions, and its real-world applications.
Understanding Quantum Computing Basics
At its core, quantum computing relies on principles of quantum mechanics, a branch of physics that governs the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels. Unlike classical computing, which processes data in discrete bits, quantum computing uses quantum bits, or qubits. These qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to a phenomenon called superposition. This property allows quantum computers to perform many calculations at once, significantly speeding up certain computational tasks.
Another fundamental principle is entanglement, where two qubits become linked so that the state of one directly affects the state of the other, no matter the distance. This allows quantum computers to process information in ways that classical computers cannot replicate. Quantum computing also leverages quantum interference, where the probabilities of quantum states can combine to amplify correct solutions while canceling incorrect ones. Together, these properties form the foundation of how quantum computing works and enable breakthroughs in computing power.
Qubits: The Building Blocks of Quantum Computing
Qubits are the heart of quantum computing, and their unique properties are what set quantum computers apart. Unlike classical bits, qubits can be in a state of 0, 1, or any combination of both at the same time. This superposition allows quantum computers to explore multiple solutions simultaneously, making them exponentially faster for certain types of problems.
Qubits can be implemented in various physical systems, including trapped ions, superconducting circuits, and photons. Each method has its own advantages and challenges. For example, superconducting qubits are widely used in commercial quantum computers due to their scalability and relatively fast operation. On the other hand, trapped ion qubits offer higher precision and stability, making them ideal for sensitive computations. Understanding qubits is crucial to grasping how quantum computing works in practice.
How Quantum Gates Manipulate Qubits
Just as classical computers use logic gates to process bits, quantum computers rely on quantum gates to manipulate qubits. These gates perform operations that change the probability amplitudes of qubits, allowing them to interact and evolve into desired quantum states. Unlike classical logic gates, quantum gates are reversible, preserving information throughout the computation process.
Quantum algorithms, such as Shor’s algorithm for factoring large numbers or Grover’s algorithm for searching databases, rely heavily on these quantum gates. By arranging quantum gates in specific sequences, quantum computers can solve problems exponentially faster than classical machines in some cases. Understanding the role of quantum gates is key to appreciating how quantum computing works beyond basic theory.
Quantum Computing vs Classical Computing
Quantum computing differs fundamentally from classical computing. While classical computers handle problems sequentially, quantum computers can tackle multiple possibilities simultaneously. This difference makes quantum computers particularly effective at optimization, cryptography, and simulating quantum systems.
However, quantum computers are not yet replacements for classical computers. They excel at specialized tasks but require extremely precise conditions, such as near-absolute-zero temperatures and protection from environmental noise. The challenges of error correction and qubit stability mean that widespread quantum computing adoption is still in its early stages. Nonetheless, ongoing research continues to push the boundaries of what quantum computing can achieve.
Real-World Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to finance. In drug discovery, quantum computers can simulate molecular interactions at a level of detail unattainable by classical machines. This could lead to faster development of new medications and treatments.
In finance, quantum computing can optimize complex portfolios and improve risk assessment models. Similarly, in logistics, quantum algorithms can enhance route optimization and supply chain efficiency. Beyond these fields, quantum computing also promises breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, materials science, and cryptography, reshaping the way we solve complex problems.
Challenges Facing Quantum Computing
Despite its potential, quantum computing faces significant challenges. Qubits are extremely sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to errors that must be corrected using sophisticated quantum error correction techniques. Maintaining stable qubits at scale remains one of the biggest hurdles for researchers.
Additionally, developing practical quantum algorithms requires deep expertise in both computer science and quantum physics. The cost of building and maintaining quantum computers is currently very high, limiting accessibility. Nonetheless, as technology advances, these challenges are gradually being addressed, bringing us closer to the era of functional, large-scale quantum computing.
The Future of Quantum Computing
The future of quantum computing holds immense promise. Tech giants and startups alike are investing heavily in quantum research, aiming to achieve quantum supremacy, where quantum computers outperform classical machines at specific tasks. As quantum hardware improves and algorithms become more refined, we may see widespread adoption in fields that demand massive computational power.
Moreover, quantum computing could redefine cybersecurity. While it threatens certain encryption methods, it also enables quantum-safe cryptography, ensuring secure communication in the future. The next decade is likely to witness breakthroughs that make quantum computing a practical tool for both industry and research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between quantum and classical computing?
Quantum computing uses qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously, while classical computing relies on binary bits of 0 or 1.
How fast are quantum computers compared to classical computers?
Quantum computers can solve certain complex problems exponentially faster, but they are not universally faster for all tasks.
What are the main challenges of quantum computing?
Challenges include qubit stability, error correction, high costs, and the need for extremely precise environmental conditions.
Can quantum computers replace classical computers?
Not entirely. Quantum computers excel at specific tasks but complement rather than replace classical systems.
Where is quantum computing used today?
It is used in research, drug development, optimization problems, cryptography, and experimental AI applications.
Embracing the Quantum Revolution
Understanding how quantum computing works provides insight into a technology poised to reshape industries and solve problems once considered impossible. While challenges remain, progress in qubit design, quantum algorithms, and error correction is accelerating. For businesses and researchers, exploring quantum computing today means preparing for the next era of computational innovation.
If you want to stay ahead in technology and discover how quantum computing can impact your field, dive deeper into research, join quantum computing communities, and explore the available platforms offering hands-on experimentation. The quantum revolution is here, and now is the perfect time to get involved.